Acoustic ISO 717-1
Rw (C ; Ctr) dB (A) 36(-1 ; -2) à 55 (-2 ; -7)
Heinen acoustic doors strictly adhere to the acoustic insulation standard ISO 717-1.
This standard summarizes airborne sound insulation with a single index (Rw). The Rw index is measured through a test conducted in an accredited laboratory.

European acoustic standards EN ISO 717-1
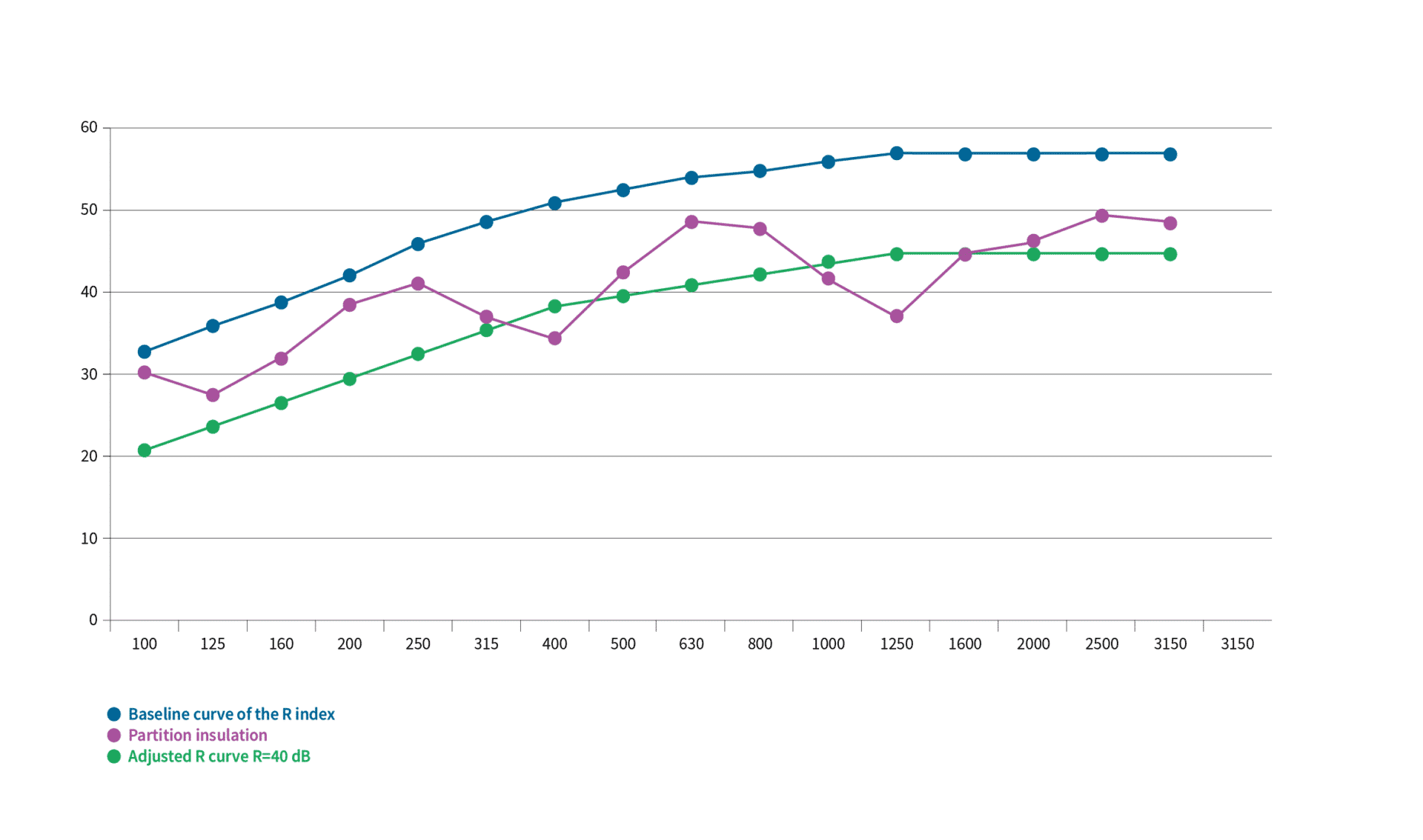
The R index, standardized by the EN ISO 717-1 standard, evaluates the acoustic quality of a partition, meaning its ability to resist the transmission of airborne sounds. It is measured only in a laboratory and only takes into account direct transmission, excluding lateral transmissions. The R index is expressed in dB(A) and is measured over the entire frequency spectrum from 100 to 4000 Hz.
The calculation of this index is done by shifting the base curve (in blue) dB by dB, until the sum of the unfavorable values (pink point under the green curve) is as large as possible but less than 10 dB across 5 octave bands (32 over 16 third-octave bands).
The Rw value of the partition is the value of the “shifted” (green) curve at 500 Hz.
Two correction indices are used to adjust the Rw index to the characteristics of the noise sources:
- C: correction for sources containing low frequencies (such as fast road traffic, children playing, or household activities).
- Ctr: correction for sources containing a lot of low frequencies (such as urban traffic, distant aircraft, or discotheques).
The acoustic attenuation index R of a partition or door is therefore expressed as: Rw (C; Ctr).
For example, a partition with an Rw (C; Ctr) = 37(-1; -3) indicates an acoustic attenuation of 37 dB for mid-frequency noises, with corrections of -1 dB for fast traffic noise and -3 dB for urban traffic noise.
Download our brochure on the EN ISO 717-1 standard to learn more about the tests and how the overall Rw value of a door is determined.
Acoustic standards table
|
EN ISO 717-1 EN ISO 140-1 |
|
|---|---|---|
| Symbols | A | |
| Resistance class | According to declared values: Rw (C; Ctr) (dB) | |
Heinen |
Single doors: Rw 36 to 55 (glazing OK) Double doors: Rw 44 to 53 |
Heinen tailors its products to your needs
If the type of noise is initially known (noise analysis), Heinen can customize a door to minimize the correction C or Ctr downwards. For example, doors for a nightclub with a lot of low-frequency noise. Additionally, Heinen offers products with combined performances. You can, for instance, have a fireproof door that is also soundproof, or a soundproof door that is also burglary-resistant. Learn more on the page dedicated to our acoustic doors.

